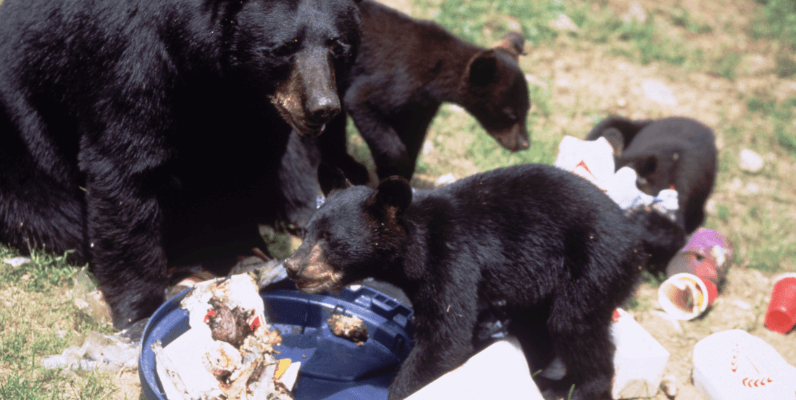
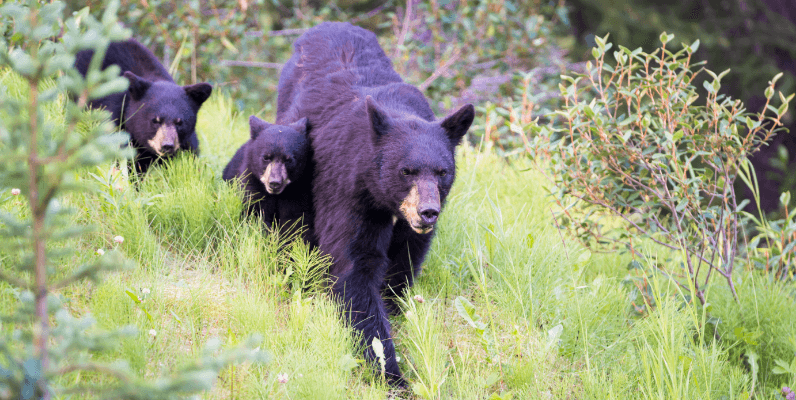
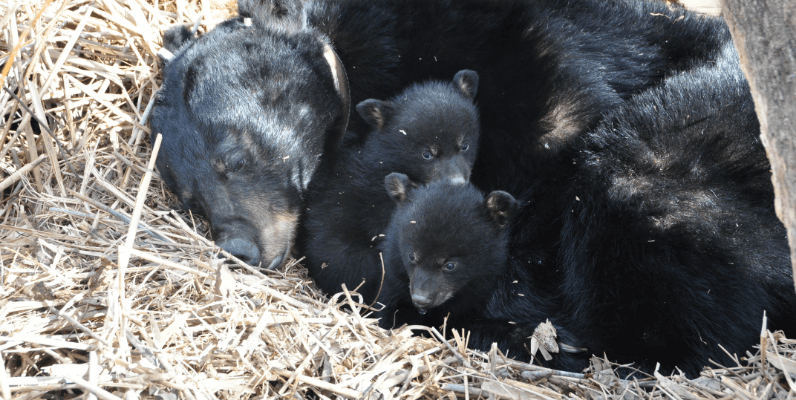
Black bears have diverse food habits, which are reflected in the different types of damage that they cause, ranging from sweet corn damage to beehive destruction. Livestock including chickens, rabbits, sheep and goats are also subject to depredation by black bears. Follow these tips to avoid attracting bears.
- Black bears are attracted to honey and will also consume bee larvae from beehives. Beehives should be located at least 50 yards from forest tree lines or other sources of cover for bears.
- Livestock feed should not be left out overnight unless enclosed in a certified bear-resistant container (www.njfishandwildlife.com/bears/garbage-management.html). Store feed in a secure building.
- Livestock pens should be located at least 50 yards from forest tree lines or other sources of cover for bears.
- Protect crops, beehives and small livestock by installing electric fencing if you live in an area with a large black bear population.
- Electric fencing is the most effective and efficient method of preventing bear damage to beehives, crops and livestock.
- Electric fencing should be simple and as strong as possible. Use an energizer with a minimum joule rating of 0.7 and a voltage output of at least 6,000 volts. Use bait on the fence. Fencing is only effective if it is maintained.
- Visit our Bear Facts for Agriculturists page for detailed fencing and maintenance instructions.
- Fish and Wildlife’s Wildlife Control Unit is available to provide technical advice with fence construction to those interested in installing electric fencing to prevent bear damage to beehives, agriculture crops and livestock.
- Depredation Permits are available to eligible farmers who are experiencing crop and livestock depredation by black bears.
- For more information, contact Fish and Wildlife at 1-877-WARN DEP (1-877-927-6337).

 Official Site of The State of New Jersey
Official Site of The State of New Jersey