Detected Species
-
HAB Species
- Diatoms
- Dinoflagellates
- Cyanobacteria
- Raphidophytes
- Haptophytes
-
Non-toxic Species
- Diatoms
- Dinoflagellates
Contact Us:
Mihaela D. Enache, Ph.D., Project Manager & Co-PI, Research Scientist I, Division of Science and Research, NJDEP (mihaela.enache@dep.nj.gov)
Ling Ren, Ph.D., PI, Research Assistant Professor, College of Science, George Mason University (lren2@gmu.edu)
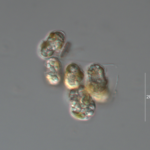
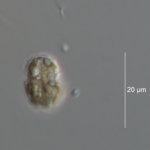
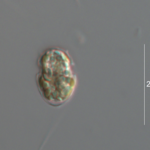
Heterocapsa niei
Morphology
Cells small, ellipsoid, 15-18 µm long, and 9-11 µm wide.
Toxins and toxicity
Its toxin production and toxicity are not known. In a recent study, three strains of Heterocapsa were isolated from a toxic HAB event in Fujian, China, including H. cf. niei. All three strains were found to be hemolytic, and all caused significant mortality of Artemia salina (Wu et al., 2022). Meanwhile, Heterocapsa pygmae, a species morphologically similar to H. niei, is known to be toxic (Hernandez-Becerril et al., 2010).
Distribution and Occurrence
Coastal and marine. In this study, it was detected abundant in PGD-2 in August 2023.
References
Wu et al. 2022. Isolation, identification and toxicity of three strains of Heterocapsa (Dinophyceae) in a harmful event in Fujian, China. Harmful Algae 120.
Hernandez-Becerril et al. 2010. Morphology of two bloom-forming or potentially toxic marine dinoflagellates from the Mexican Pacific, Heterocapsa pygmae and Protoceratium reticulatu (Dinophyceae). Cryptogamie, Algologie, 31: 245-254